
INDUSTRY UPDATE: Female Executives
Women appear to be making progress in increasing their share of the C-suite. Specifically, the evidence suggests that 26% of CEOs and Managing Directors in 2021 were women as opposed to 15% in 2019. [See source.] Barrett Group research supports this notion, showing an improvement from 24% to 25% in the female share for all executive categories between 2022 and 2023. [See Editor’s Note.]
What factors are driving this change and where will they lead?
Attention to gender diversity often begins in the board room. “Although these gender disparities exist in boardrooms globally, they also can vary depending on where the company is based. For example, Europe has the highest representation of women on boards at 35 percent, while the Middle East has one of the lowest with only 10 percent of seats held by women, according to Deloitte. Globally, publicly listed companies have a better representation of women on boards (19.7 percent) when compared to US-venture backed private companies (7 percent).” [See source.]
On the other hand, some private equity firms have made diversity a key principle even setting specific targets and reporting on their progress publicly, such as BlackRock, one of the biggest PE firms. Here is what BlackRock says: “Hiring is a leading indicator of the future composition of our employee base and management. In 2021, 47% of our hires and 38% of the senior hires (Directors and above) were women.” [See source.]
If diversity is your principal requirement, then perhaps this ranking may help: Diversity Inc. This firm claims to perform an exhaustive review on multiple parameters to establish which companies are the most diverse. Their top five include: Accenture, Mastercard, Abbott, Toyota Motor North America, and Eli Lilly and Company. Here is what number one ranked Accenture has to say on the subject: “Our commitment starts at the top – 60% of our board of directors are racially and ethnically diverse, and 50% are women including our Chair and CEO Julie Sweet.” [See source.]
The World Bank cites investor pressure as one of the main reasons for the progress women are making, but there may be additional reasons beyond ESG [See source]. Perhaps companies simply need different skills these days in their top management. That is the post-pandemic line of argument offered by this Forbes article: “It means resilience, empathy, agility, ability to articulate, communicate, inspire people, keep people moving forward in very difficult times. All those are skills that a lot of CEOs have had in the past, but they’ve really moved to the forefront.” This logic goes on to suggest that women have been siloed in human resources and sustainability roles historically, but that the skills required for these roles are now even more required in the C-suite. [See source.]
Another line of argument is more provocative: “If you think that men make better leaders, not only do we disagree, but we have the data to back it up! The 32 companies that have women as CEOs have significantly outperformed the companies run by men. Over the past 10 years, the difference in returns is 384% from female-led companies vs. 261% from male-led companies. A few notable companies with women CEOs are GM, UPS, Citigroup, and CVS.” [See source.]
As far as compensation is concerned, the US Bureau of Labor Statistics published Q4 2022 survey data that found women are now earning on average about 83% of what men earn, a ratio that has remained relatively constant over the last few years. (See source.) However, another source claims that female managers as a class of employees now earn approximately 90% of their male counterparts’ pay. In fact, according to the same source, if the income survey results are controlled for equivalent roles, responsibilities, and titles, the pay gap narrows further to just 1%. (See source.) In Europe, “The gender pay gap in the EU stands at 13.0 % in 2020 and has only changed minimally over the last decade. It means that women earn 13.0 % on average less per hour than men.” (See source.)
“Women leaders switch jobs at record rates as they demand better from their workplaces” “Women leaders are saying effectively, ‘We’ve had enough,’ […] ‘We’re ambitious. We want successful careers. But we’re going to go look for organizations that are delivering the work culture that we also want.’ “[See source.]

Of course, biology offers women more choices and more constraints than men.
Obviously, men are not capable of bearing children. This fact has often relegated women to a set of activities and specific roles in many cultures since before we were fully homo sapiens. In general, this has also meant that as education and wealth increased, women tended to have fewer children for various reasons, including the ability to focus on their professional advancement. However, recently, as child care, parental leave, and other benefits have evolved, this pattern has begun to shift so that birth rates are again rising in some of the world’s wealthiest countries. [See “In rich countries, working women and more babies go hand in hand”, the Economist, August 23, 2022.]
On balance then, female business leaders have certainly made some progress, however, employers still have a long way to go to achieve real parity for the sexes at the executive level. For example, in the latest ranking, only 8.2% of the CEOs in the S&P 500 are women [See source]. Indeed, gender shares also vary significantly by industry, role, and location as we will see in some detail later in this Industry Update.
In fact, some women are not waiting for companies to catch up but are simply heading for the door according to a report in Q4 2022 titled “Women leaders switch jobs at record rates as they demand better from their workplaces.” [See source.] This source continues, “Rachel Thomas, the CEO of LeanIn.Org, says that while women leaders are just as ambitious as men, they are leaving their companies — for a number of reasons — at “the highest rate we’ve ever seen.” For every woman at the director level who gets a promotion, two women directors are voluntarily leaving their organization […] “We already know women are underrepresented in leadership, and now companies are starting to lose the precious few women leaders they do have.”” [See source.]
Changing jobs can also bring economic rewards, of course: “Women who found new jobs during the pandemic were slightly more likely to see an increase of over 30% in compensation than men […] For senior-level employees, switching jobs had the biggest pay off. More members of this group — which includes vice presidents, C-suite employees and CEOs — experienced compensation increases of 30% or higher (35%) than other individual contributors who changed jobs during the pandemic (22%).” [See source.]
Let us find out more about the progress women are making at all corporate levels as we explore the facts in this Industry Update.
The Female Executive Market
LinkedIn does not specifically record gender or report on the gender balance at individual companies, so we will need to infer some of our data by looking at the total executive market and the average female share. In these terms, LinkedIn reports 2.15 million women executives as we define them in our target geographies (see Editor’s Note)—25% of the 8.5 million total executive population. Approximately 1.3 million women executives are in the US (27% of total executives), while 821,000 are in the EU and UK (22% of total) and 77,000 (17%) work in the Middle East. We cannot distinguish specific growth rates for women executives, but the overall executive market has grown by 0.8% (1% in the EU/UK and Middle East and 0.7% in the US), while a further 331,000 have changed jobs, leading to a total (male and female) of some 400,000 executive opportunities in the past year.
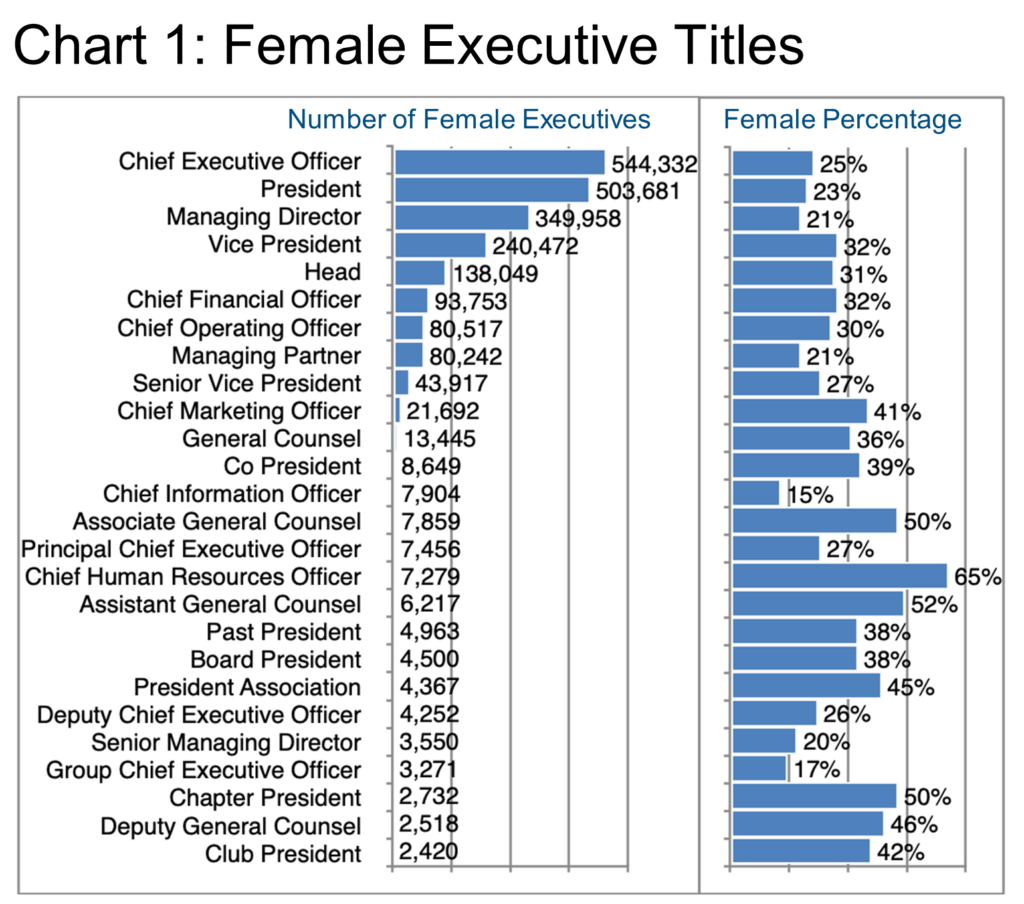
Selecting titles in descending order by the number of female executives, Chart 1 says for example that there are more female CEOs than any other title, but that these female CEOs represent only about 25% of the total number of CEOs in our target geography per LinkedIn. Conversely, Chief Human Resource Officers are apparently predominantly female (65%) although there are relatively few of them at 7,279.
The common wisdom seems to be that women are more empathetic and effective in dealing with the emotional territory of human resources, however, that does not explain why women also tend to occupy more executive marketing or general counsel positions.
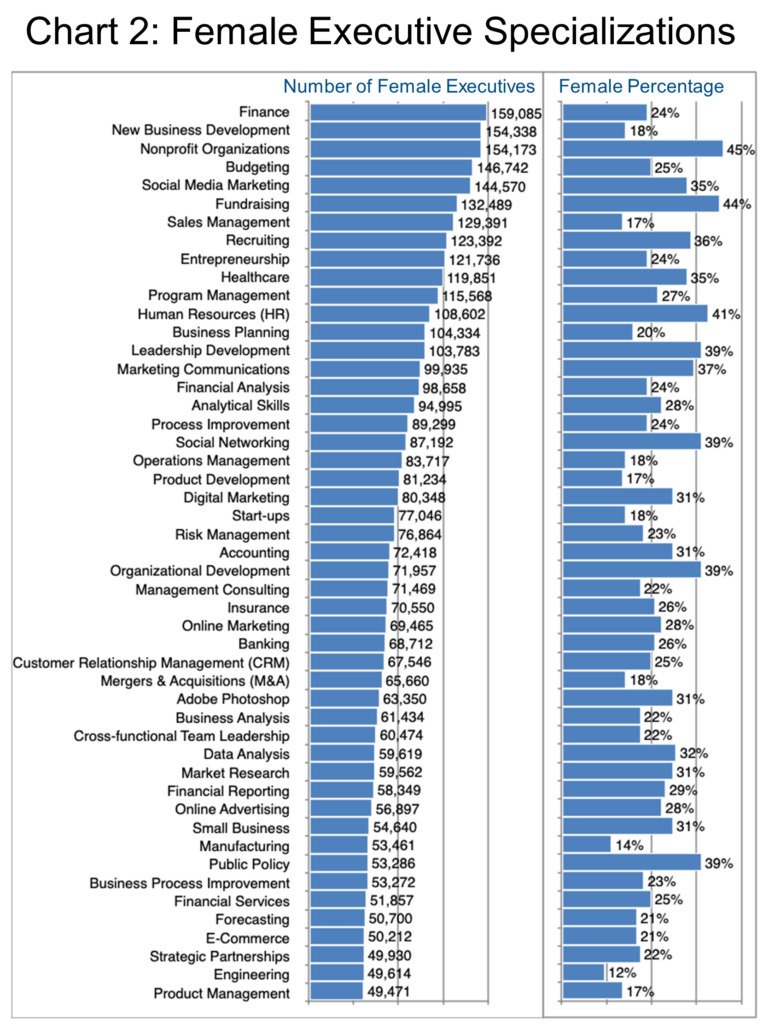
In some ways, Chart 2 might be seen to debunk those preconceived notions by showing New Business Development as the second most frequent female executive specialization until you notice that only 18% of these professionals are female. This area along with Sales Management tends to be quite well-remunerated, and in both cases the female executive share is quite low (17-18%). If any specialization requires emotional intelligence, surely sales and business development do. So why are there as yet relatively few women executives in these critical roles?
Areas where women’s shares stand out include Nonprofit Organizations, Fundraising, Human Resources, Leadership Development, Marketing Communications, Social Networking, Organizational Development, and Public Policy. In general, these all do tend to require people skills, but then how do we explain that Finance and Budgeting occupy two of the top five spots, skills are long known for a focus on facts?
The simple answer is probably that women occupy roles that organizations make available to them, and not because of any innate proclivities based on gender, so, as we addressed in the introduction, it is indeed management attitudes that most closely define where women can develop professionally. In that sense, the evolving view from the board room and the inspiring examples set by current female CEOs—these will determine the future and the weight of precedent should continue to lessen over time.
LinkedIn does not provide the gender share for individual companies, so it is difficult to address this parameter except by bringing in external, specialist perspectives. We have already referred in the introduction to one excellent source on this subject, Diversity Inc., that publishes a ranking of the most diverse companies, although gender share is not their only criterion.
In fact, Diversity Inc.’s top ten ranking covers a surprisingly broad range of industries, including IT Services, Financial Services, Healthcare, Automotive, Food, Media & Entertainment, Insurance, and Medical Devices. In other words, increasingly it appears that if you as an executive do not appreciate your employer’s culture, you have a choice.
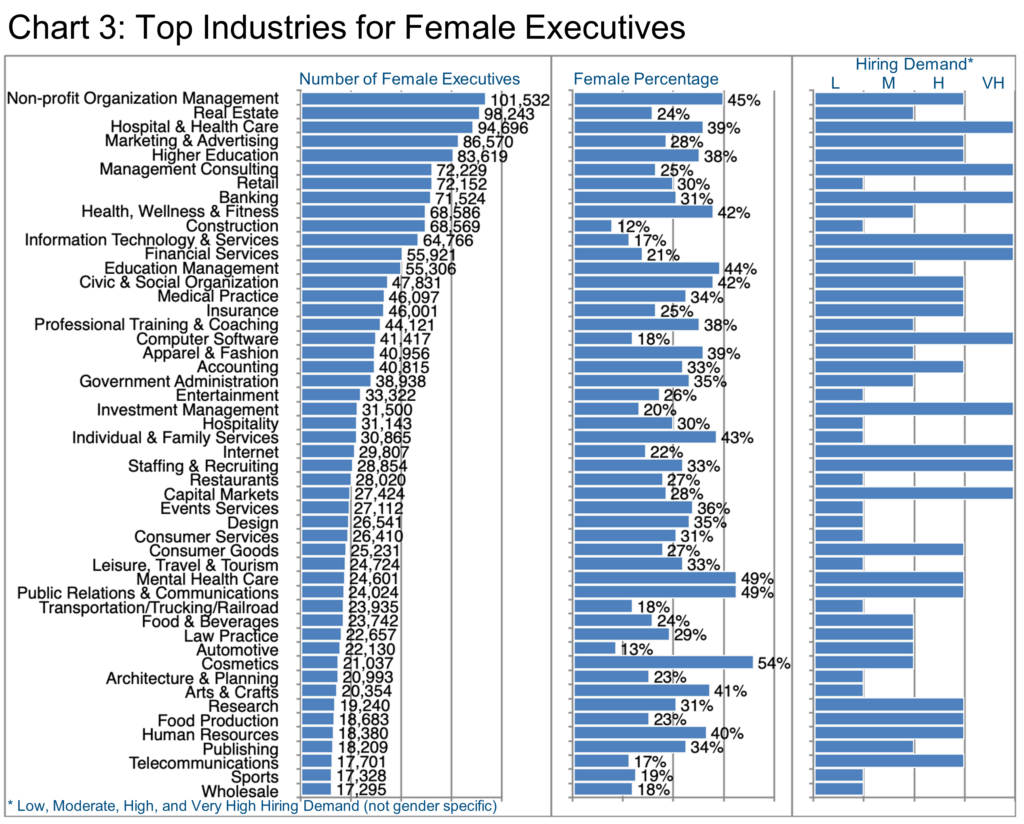
Chart 3 covers the industries with the most female executives, their gender share, and the relative hiring demand (for all genders) in that sector according to LinkedIn. For example, Non-profit Organization Management as an industry employs the most female executives in total and boasts a 45% female share among its executives—quite high by comparison to others on the chart—while LinkedIn rates the hiring demand in this sector as “high.”
Perhaps understandably, Cosmetics demonstrates the highest female executive share (54%) although incumbents number only about 21,000 and the hiring demand seems to be “moderate.”
Mental Health Care and Public Relations & Communications are also relatively small in total volume of female executives, though their female shares are high (49% each), and the hiring demand is rated as “high.”
Barrett Group clients, of course, have access to considerably more detailed information on industries, companies, and even hiring executives, but even if you are embarking on a search without professional support, always perform adequate research first! For example, the very high hiring demand in several industries in Chart 3 could make them more attractive if you have affinity for their sphere of activity.
The Barrett Group routinely helps executives change industries, roles, and locations by helping them to articulate the transferability of their skills and experience persuasively. Gone are the days that an executive was wedded to a specific industry simply because that is where her professional history lay.
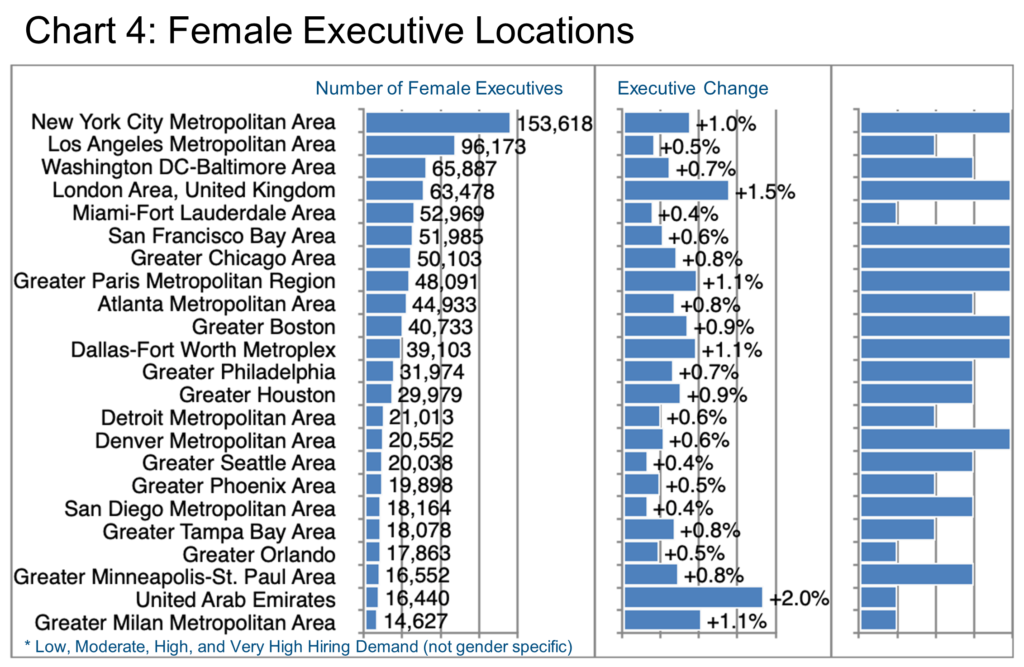
That applies to location, too, of course. Chart 4 provides an overview of which locations have the largest female executive populations. Note that the Executive Change data is for female and male executives as is the Hiring Demand data because LinkedIn does not separate these data points by gender.
If you are feeling more entrepreneurial, you may find a ranking such as this one (Best Cities for Female Entrepreneurs) useful, but other rankings look at housing, benefits, educational opportunities, etc. Again, our advice is to never stint on research when making an important career decision. For Europe, this ranking is also of interest, factoring in quality of life along with many other variables: Top Six Cities of Quality of Life, though perhaps not only for female executives. As far as the overall gender share is concerned in European cities, this interesting source suggests that Riga, Vilnius, Lisboa, Madrid, Porto, Budapest, Zagreb, and Genoa have the highest overall share of women in their populations.
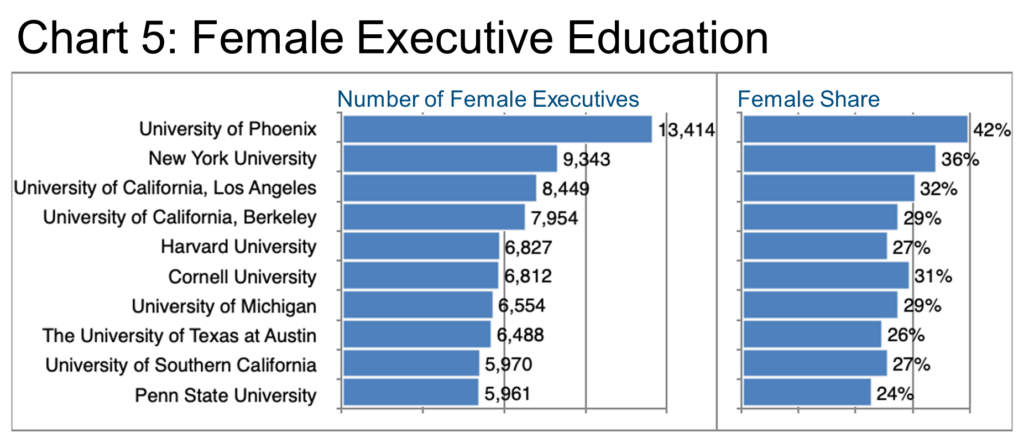
Education (Chart 5, Top 10 universities by number of female execs) may also be career-relevant, though it seems odd to see the first European schools joining this ranking at number #26 (Cambridge), #32 (Oxford), #38 (London, LSE), and #39 (Universidad Complutense de Madrid), and all of these latter four have rather low female shares by comparison to the top ten. Nevertheless, educational institutions can be powerful factors in intentional career networking, and are not to be taken lightly.
Peter Irish, CEO
The Barrett Group
Click here for a printable version of this Industry Update – Female Executives 2023
Editor’s Note:
In this particular Update “executives” will generally refer to the Vice President, Senior Vice President, Chief Operating Officer, Chief Financial Officer, Managing Director, Chief Executive Officer, Chief Human Resources Officer, Chief Marketing Officer, Chief Information Officer, Managing Partner, General Counsel, Head, and President titles. Unless otherwise noted, the data in this Update will largely come from LinkedIn and represents a snapshot of the market as it was at the time of the research.
Is LinkedIn truly representative? Here’s a little data: LinkedIn has more than 900 million users. (See source) It is by far the largest and most robust business database in the world, now in its 20th year. LinkedIn defines the year-over-year change (YOY Change) as the change in the number of professionals divided by the count as of last year and “attrition” as the departures in the last 12 months divided by the average headcount over the last year.












